Derivatization in HPLC
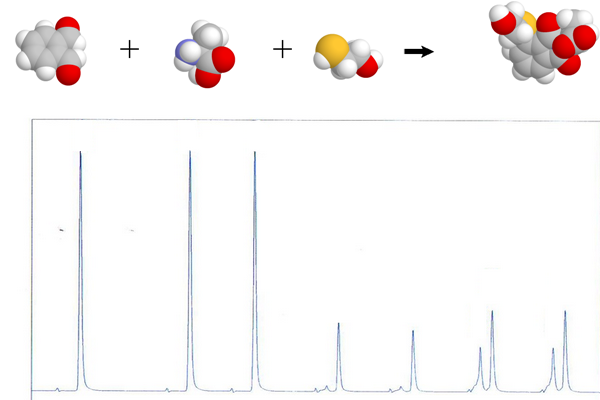
HPLC is a method of choice for the qualitative and quantitative determination of organic and inorganic substances into different kind of matrices. Unfortunately, many substances of interest cannot be directly analyzed in HPLC because they do not include the necessary UV chromophores, fluorophores or redox groups for the detection.
Derivatization is able to introduce these groups into sample molecules in order to increase their sensitivity to UV absorption and fluorescence detection. Derivatization can be obtained by organic or electrochemical reactions, such as oxidation and reduction, or by displacement or addition reactions.
The derivatization reaction can be performed manually in vials before injection into LC system, but the process can also be automated in order to reduce sample preparation time and increase the process standardization (in terms of precision of the reagent dispensation and homogeneity of the reaction time) for the best reproducibility.
That’s why HPLC autosamplers that are able to perform sample derivatization are advisable for many kinds of HPLC analysis: find out the HTA solution for both Sample derivation and HPLC injection.
Latest News
- The Importance of a Good Distributor in the Lab Industry
- HOW TO VIDEO: run calibration in your HTA Spectroscopy Autosampler
- HTA: New Spaces for a New Era
- Case Study: Contract Testing Laboratories with Multiple Locations
- Our New Headquarters: We Go Green
- Dear HTA, My Christmas wish is…
- Case Study: Future-Proofing Investments for Public Research Laboratories
- Flow Cytometry Analysis: New frontiers in Allergy Testing
- Infinite sample capacity autosampler
- HOW TO VIDEO: replace the syringe in your HTA GC autosampler



